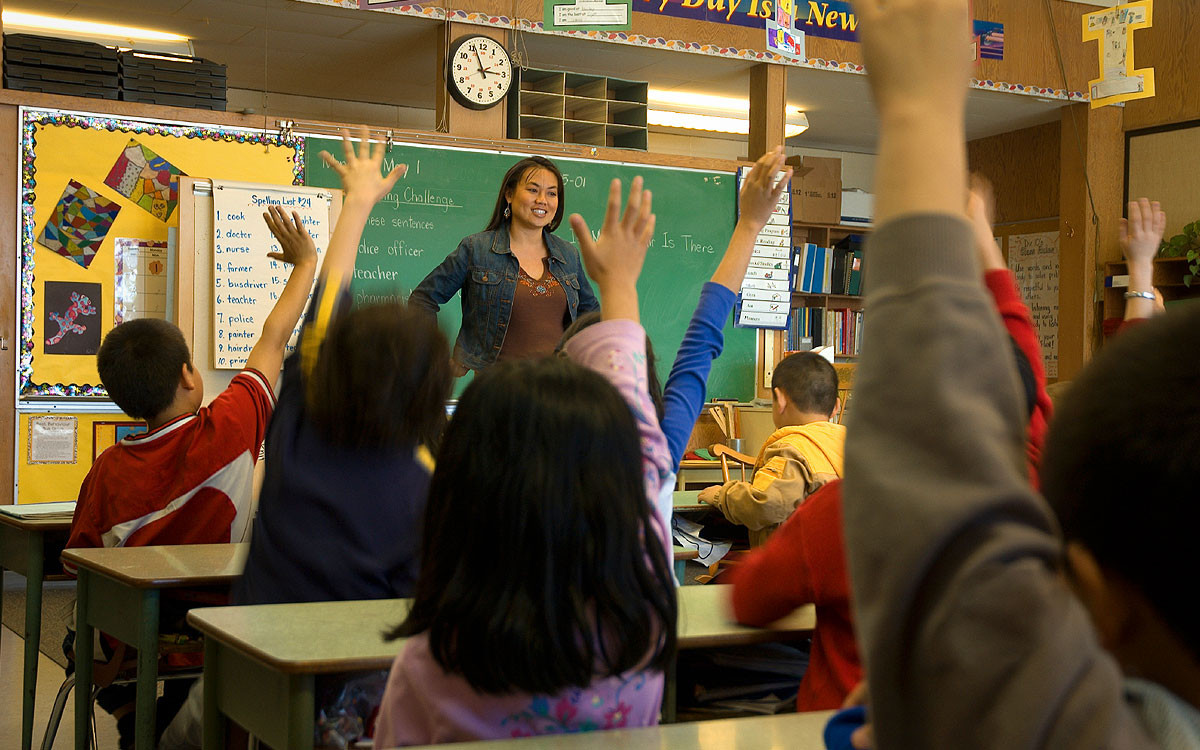
As students and teachers head back to school all over the country, we wanted to share some ideas on how Flipboard can be helpful this school year. Since the launch of Flipboard 2.0 this past spring, our readers can collect articles and turn them into shareable magazines. We’ve found that educators are doing this a lot—for class reading assignments, student projects and their own enlightenment.
Here’s how you can use Flipboard in teaching and learning:
1. Keep up on current events: Flipboard has more than 125 publishing partners, including the BBC, New York Times, TechCrunch, Vanity Fair and Harper’s Bazaar, as well as sections curated around topics such as News, Tech, Travel and Design—”one-stop shops” for authoritative news on a subject. Tap on the red ribbon to explore great magazines, newspapers and blogs in the Content Guide.
2. Create a class syllabus: Plan out the semester for your students by making your syllabus available in a magazine. Include articles and editorial content that your students need to read throughout the semester to ensure success in your class. You can supplement it with your own notes by using a blogging platform such as WordPress, and flipping your posts into your magazine. Encourage students to comment on articles to track engagement.
Things AP Econ Students Should Know: by Michael Brody
3. Class projects: Task your students with creating a class-project magazine. Have them compile editorial, images and YouTube videos around specific subject matter they’re studying in your class. They can do this individually, or in groups (tap “Invite Contributors” from the magazine’s front page.)
Government Class: by kimberleyscox
Mike McCue: by Brian Pinkston
4. Educational Resource Guides: The education process is never ending. Create a resource guide by compiling articles and educational materials on a single topic or general areas of inquiry and share that with your colleagues.
Science class: by Zach Morrow
EducAtion: by Brendan Gilligan
Early Childhood Education: by Jacqueline Mezquita
5. Collaboration: Teaching is all about teamwork. Invite other educators to collaborate on a resource guide or have your students collaborate on a magazine for class. Compile articles, teaching resources or how to videos related to the subject you teach or education in general and share that magazine with other educators in your school or district.
Student Blogging Challenge Sept 2013: by suewaters
Education & Educapability: by Joshua Hostetter
6. Keep parents informed: Stay in touch with your classroom parents by creating a magazine with curriculum examples, class readings, suggested at home projects, images from class and classroom updates flipped in from a personal blog. Encourage your parents to subscribe to the magazine to stay up to date on everything going on in your classroom.
7. Your school, on the go: For administrators—Flipboard is a great way for your school to stay in touch with students, parents and the community. As long as your school paper, newsletter or event images are available as an RSS feed or via social media, you can search for it on Flipboard. You can also use our Web tools to flip your school’s posts into new magazines—into which you can even mix in other content—around any topic you like.
The Paly Voice: by Callie Walker
Flipboard has previously teamed up with both TeachThought and EdReach, two great educational organizations, to teach their networks how educators and students can best use Flipboard. Check out both of these resources for some additional tips and tricks.
And to learn more about how educators are using Flipboard, from educators, check out these blog posts:
Happy school year to everyone!
~CarolynG
/flipboard
@flipboard
+flipboard